Diabetic ulcers are a common and serious complication of diabetes. They are open sores or wounds that develop on the feet or lower legs of individuals with diabetes. These ulcers can be painful, slow to heal, and may lead to severe complications if not properly treated. In this article, ozinsight will delve into the details of diabetic ulcers, including their causes, symptoms, treatment options, and preventive measures.
What is a Diabetic Ulcer?
A diabetic ulcer is a skin lesion that occurs due to poor blood circulation, nerve damage, and reduced immune function in individuals with diabetes. High blood sugar levels over time can cause damage to the nerves (neuropathy) and blood vessels (vascular disease), particularly in the lower extremities. This combination of neuropathy and vascular disease makes individuals with diabetes more prone to developing ulcers, especially on the feet.
Causes of Diabetic Ulcers
Diabetic ulcers can have various causes, including:
- Neuropathy: Nerve damage in the lower extremities reduces sensation, making it difficult to detect injuries or pressure points.
- Vascular disease: Poor blood circulation impairs the delivery of nutrients and oxygen to the affected area, hindering the healing process.
- Foot deformities: Conditions like hammertoes, bunions, and Charcot foot can increase the risk of developing ulcers.
- Trauma: Even minor injuries, such as blisters, cuts, or abrasions, can lead to ulcers if left untreated.
- Poor wound healing: Diabetes affects the body’s ability to repair and regenerate damaged tissues, making ulcers more likely to develop and persist.
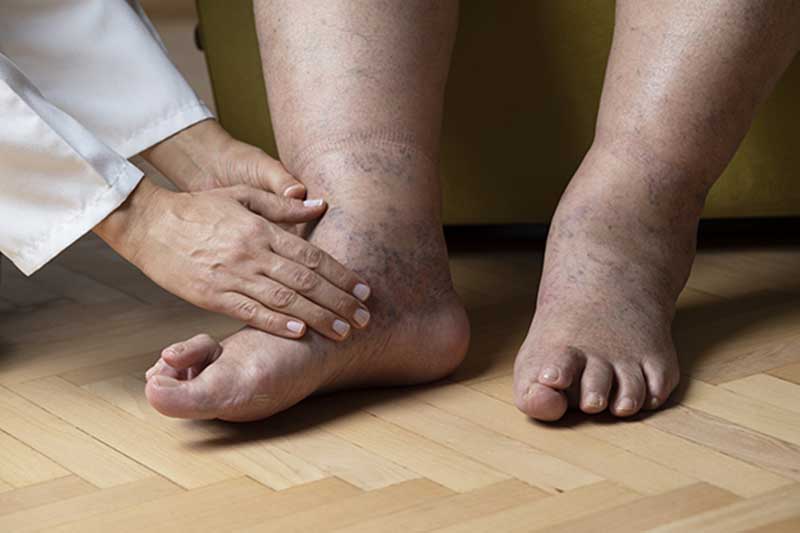
Symptoms and Warning Signs
Recognizing the early signs of a diabetic ulcer is crucial for timely intervention. Common symptoms and warning signs include:
- Redness, swelling, or tenderness around a specific area.
- Persistent drainage or discharge from the wound.
- Foul odor emanating from the ulcer.
- Changes in skin color or texture around the affected site.
- Development of a callus or thickened skin over the ulcer.
- Pain or discomfort, particularly when walking or applying pressure to the area.
Complications of Diabetic Ulcers
Neglected or improperly managed diabetic ulcers can lead to severe complications, such as:
- Cellulitis: Bacterial infection that spreads to the surrounding tissues.
- Osteomyelitis: Infection of the bone underlying the ulcer.
- Gangrene: Death and decay of the affected tissues.
- Lower limb amputation: In extreme cases, when the ulcer becomes non-healing or severely infected, amputation may be necessary.
Diagnosis and Treatment Options
Prompt diagnosis and appropriate treatment are essential for managing diabetic ulcers effectively. A healthcare professional will conduct a thorough examination and may perform additional tests, such as:
- Evaluation of blood circulation and nerve function.
- Imaging tests, like X-rays or MRI scans, to assess the depth and extent of the ulcer.
- Cultures to identify the presence of infection.
Treatment options for diabetic ulcers may include:
- Wound debridement: Removal of dead or infected tissues to facilitate healing.
- Dressings and bandages: Application of specialized dressings to create a moist environment and protect the ulcer from further damage.
- Offloading: Reducing pressure on the ulcer through the use of supportive footwear, braces, or crutches.
- Medications: Antibiotics to treat or prevent infection, and topical creams or ointments to promote healing.
- Advanced therapies: In some cases, advanced techniques like hyperbaric oxygen therapy or growth factor therapy may be recommended.
Prevention and Management
Prevention plays a crucial role in reducing the incidence of diabetic ulcers. Proper foot care and diligent management of diabetes can significantly lower the risk. Here are some preventive measures:
- Regular foot inspections: Checking for any signs of redness, blisters, or cuts and seeking prompt medical attention if detected.
- Proper hygiene: Keeping feet clean and dry to prevent infections.
- Moisturization: Using a moisturizer to prevent dry skin and cracks.
- Appropriate footwear: Wearing well-fitting shoes and avoiding tight or pointed-toe designs.
- Regular exercise: Engaging in physical activity to improve blood circulation.
- Blood sugar control: Maintaining optimal blood glucose levels through medication, diet, and lifestyle modifications.
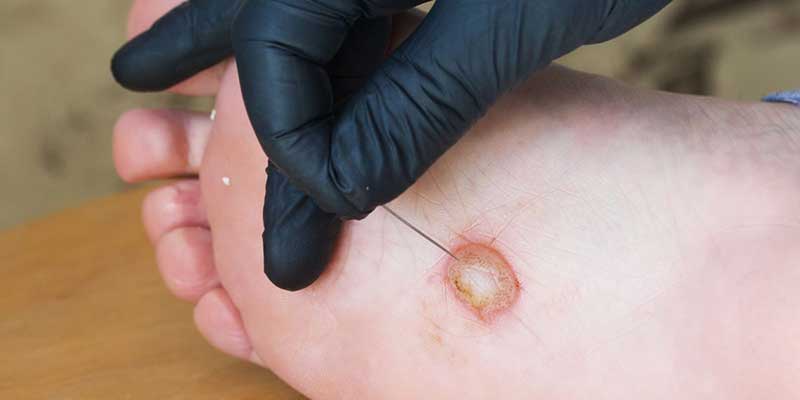
Lifestyle Changes for Diabetic Ulcer Prevention
In addition to specific preventive measures, certain lifestyle changes can contribute to overall diabetic ulcer prevention:
- Healthy diet: Consuming a balanced diet rich in nutrients, including fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins.
- Smoking cessation: Quitting smoking reduces the risk of vascular disease and improves overall health.
- Weight management: Maintaining a healthy weight can alleviate pressure on the feet and lower the risk of ulcers.
Diabetic Ulcer Care at Home
While medical intervention is crucial, caring for diabetic ulcers at home can support the healing process. Some home care tips include:
- Cleaning the ulcer with mild soap and water as directed by a healthcare professional.
- Applying prescribed topical medications or dressings.
- Protecting the ulcer with appropriate footwear or bandages.
- Elevating the affected limb to reduce swelling and improve blood flow.
The Role of Diet in Diabetic Ulcer Management
A well-balanced diet plays a significant role in managing diabetic ulcers. Consider the following dietary guidelines:
- Adequate protein intake: Protein is essential for tissue repair and wound healing.
- Vitamin and mineral-rich foods: Vitamins A, C, and E, as well as zinc and selenium, are vital for skin health and wound healing.
- Omega-3 fatty acids: Found in fish, flaxseeds, and chia seeds, they possess anti-inflammatory properties.
- Controlled carbohydrate consumption: Balancing carbohydrate intake helps manage blood sugar levels.
The Importance of Regular Medical Check-ups
Regular medical check-ups are essential for individuals with diabetic ulcers. These check-ups allow healthcare professionals to:
- Monitor the healing progress of the ulcer.
- Adjust treatment plans as needed.
- Address any potential complications.
- Provide ongoing education and support.
Support and Resources for Diabetic Ulcer Patients
Living with diabetic ulcers can be challenging, both physically and emotionally. Seek support from the following resources:
- Diabetes support groups: Connect with others facing similar challenges and share experiences.
- Wound care clinics: Specialized clinics that offer comprehensive care for individuals with diabetic ulcers.
- Healthcare professionals: Consult with doctors, nurses, and wound care specialists for guidance and treatment.
Emotional and Psychological Impact
Dealing with diabetic ulcers can take a toll on a person’s emotional well-being. It is important to address the emotional and psychological impact by:
- Seeking professional counseling or therapy.
- Engaging in stress-reducing activities, such as meditation or hobbies.
- Building a strong support network of family and friends.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Can diabetic ulcers be prevented?
Yes, proper foot care, blood sugar control, and healthy lifestyle choices can help prevent diabetic ulcers.
How long does it take for a diabetic ulcer to heal?
The healing time can vary depending on the severity of the ulcer and individual factors. It can range from weeks to several months.
Can diabetic ulcers recur?
Yes, without proper management and preventive measures, diabetic ulcers can recur.
Are there any home remedies for diabetic ulcers?
While home care can support the healing process, it is essential to seek medical advice for appropriate treatment.
Can diabetic ulcers be contagious?
No, diabetic ulcers are not contagious. However, if left untreated, they can lead to severe infections.
Conclusion
Diabetic ulcers are a significant concern for individuals with diabetes. Understanding their causes, symptoms, and treatment options is crucial for timely intervention and effective management. By adopting preventive measures, seeking medical care, and making necessary lifestyle changes, individuals with diabetes can reduce the risk of developing ulcers and prevent potential complications. Remember, early detection and comprehensive care are essential for maintaining foot health and overall well-being.













Got a Questions?
Find us on Socials or Contact us and we’ll get back to you as soon as possible.